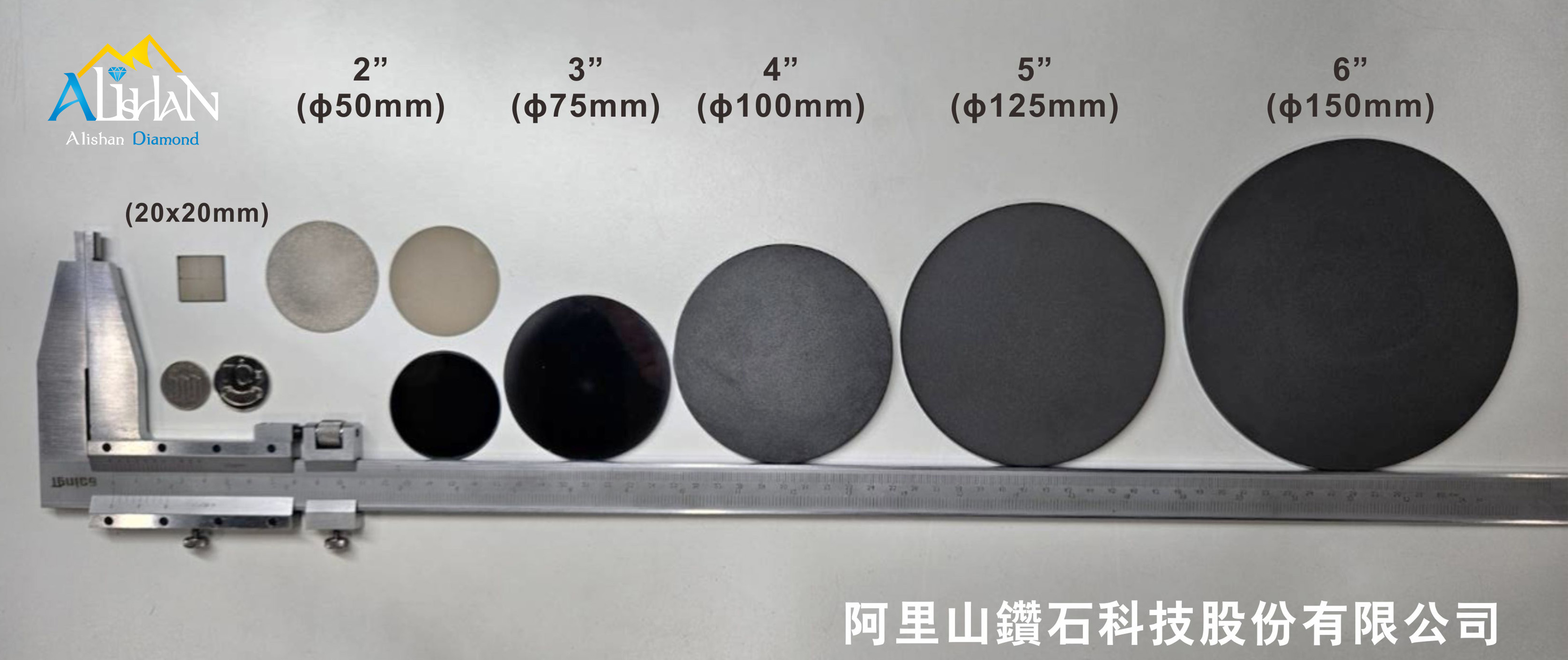
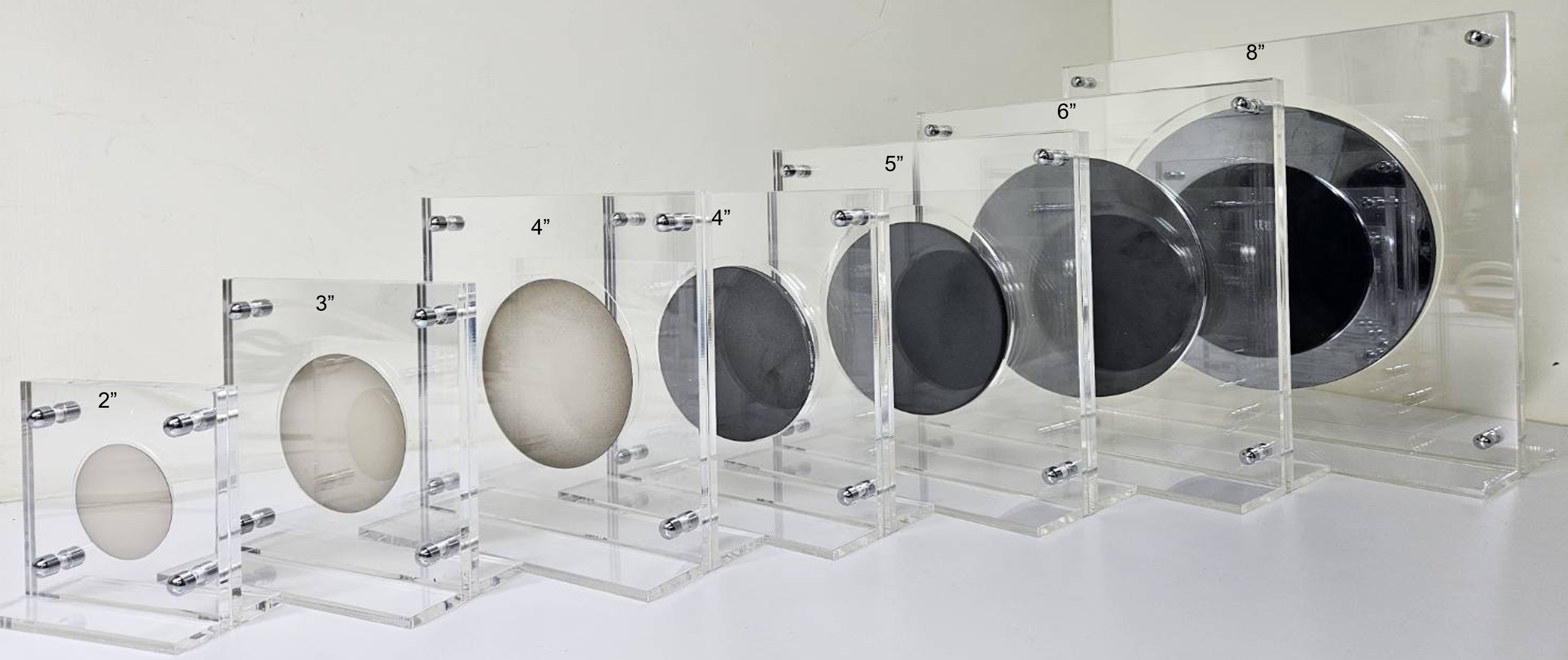
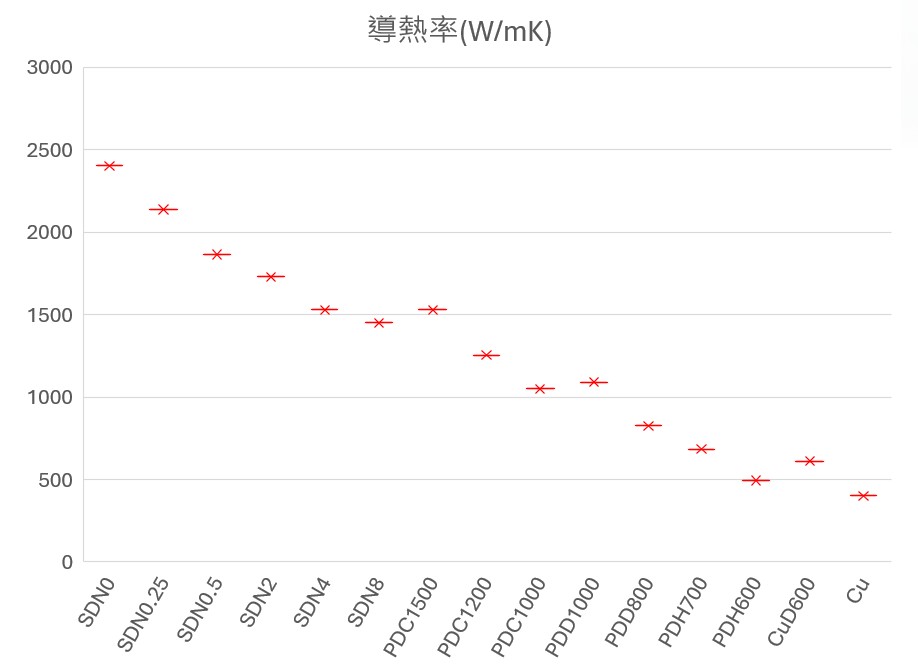
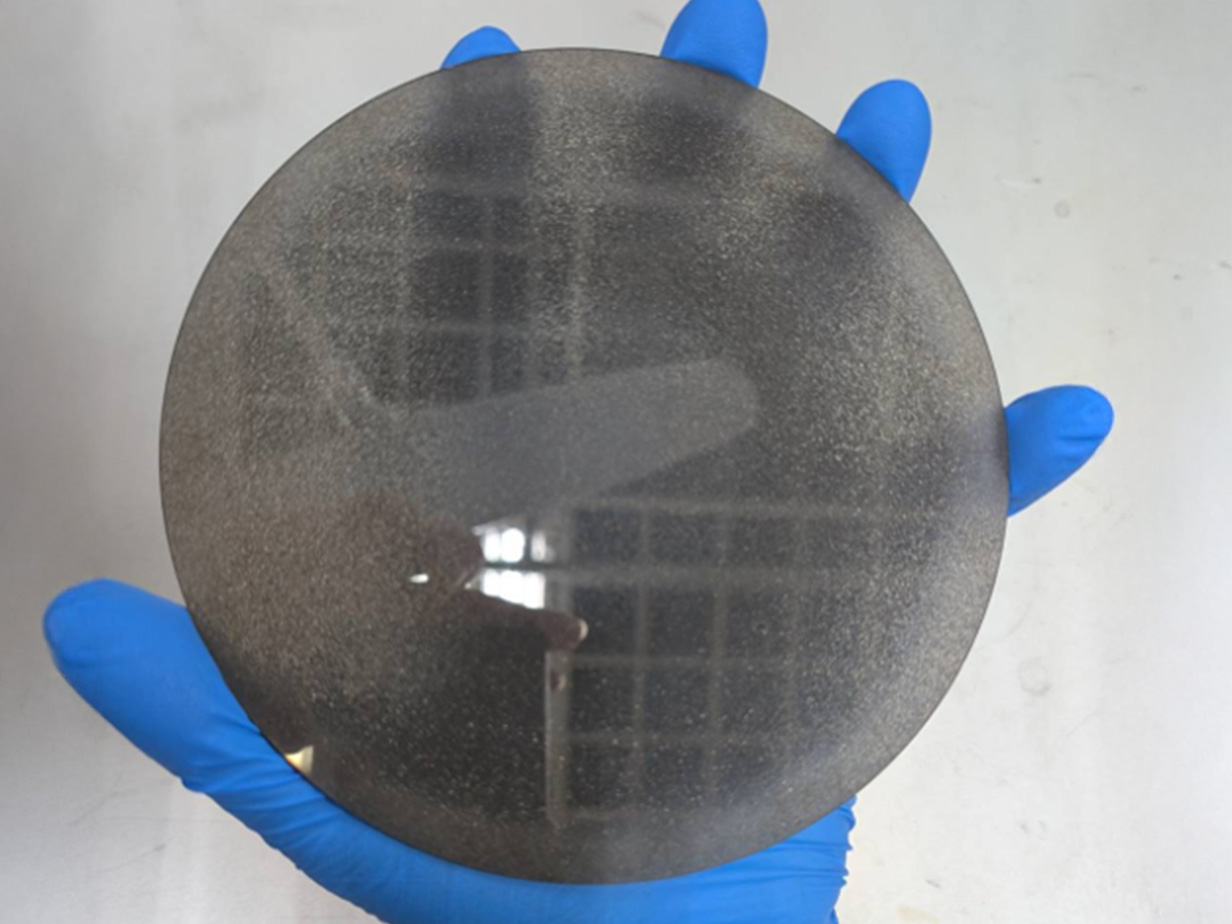
Diamond Wafer/Substrate
Diamond Wafer/Substrate
The Diamond Wafer marks a significant milestone in semiconductor technology, symbolizing the transition from the “silicon era” to the “carbon era.”
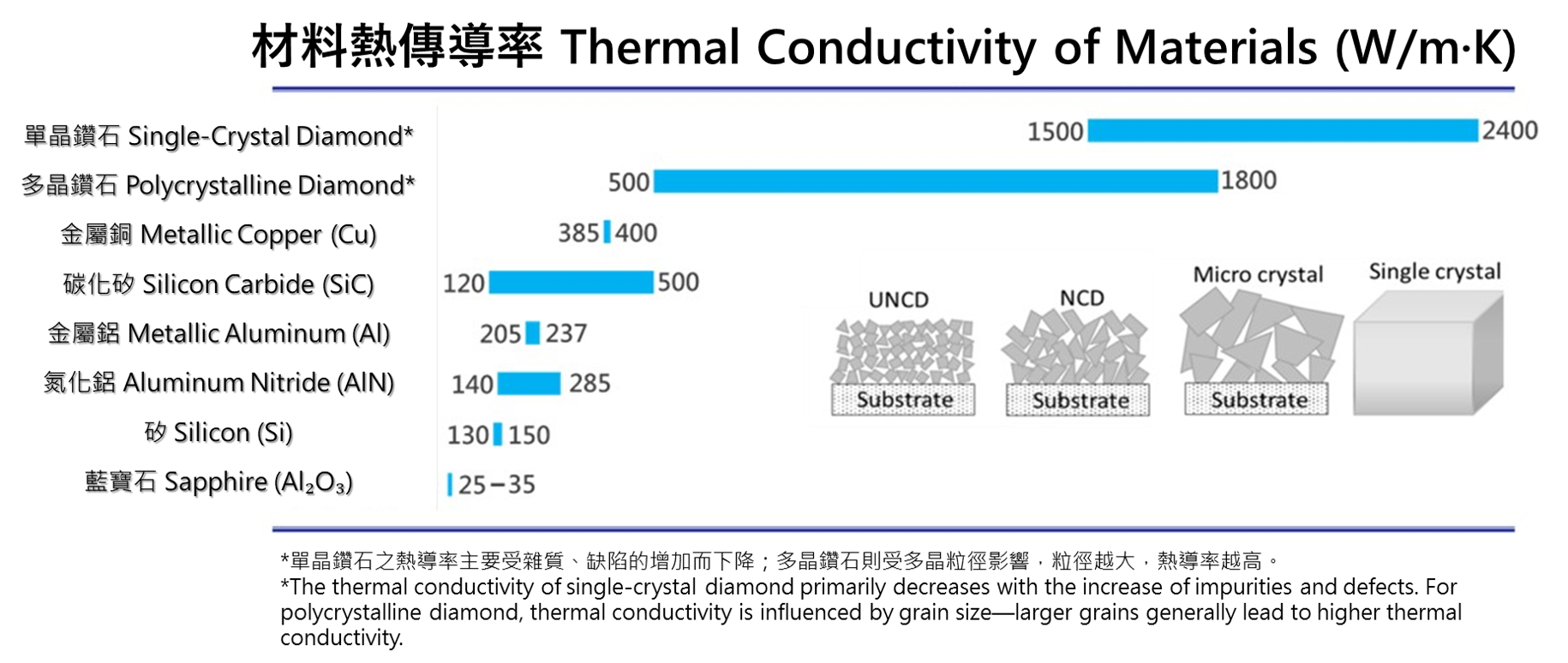
Diamond technology applications span across multiple fields, including thermal management, optics, semiconductors, tools, biomedicine, quantum technology, and energy. Its core values lie in its high thermal conductivity, extreme hardness, optical transparency, biocompatibility, and quantum properties. With continuous advancements in diamond cultivation technology, the cost of diamond materials is gradually decreasing, and their application scope and market potential will continue to expand.
|
Category |
Single-Crystal Diamond |
Polycrystalline Diamond |
|
Thermal conductivity |
≧ 2000 W/(m·k) |
1000~2000 W/(m·k) |
|
Thermal expansion coefficient |
1.1x 10 -6 /℃ |
3.1962x 10 -6 /℃ |
Applications
- Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs): Used between chips, modules, and heat sinks to reduce thermal resistance and improve heat transfer efficiency.
- Electronic Packaging and Substrates: Provides outstanding thermal management in semiconductor packaging, enabling devices to operate under higher power density conditions.
- LEDs, Optoelectronics, and Related Components: Enhances thermal performance of optoelectronic devices, extending lifespan while improving brightness and efficiency.
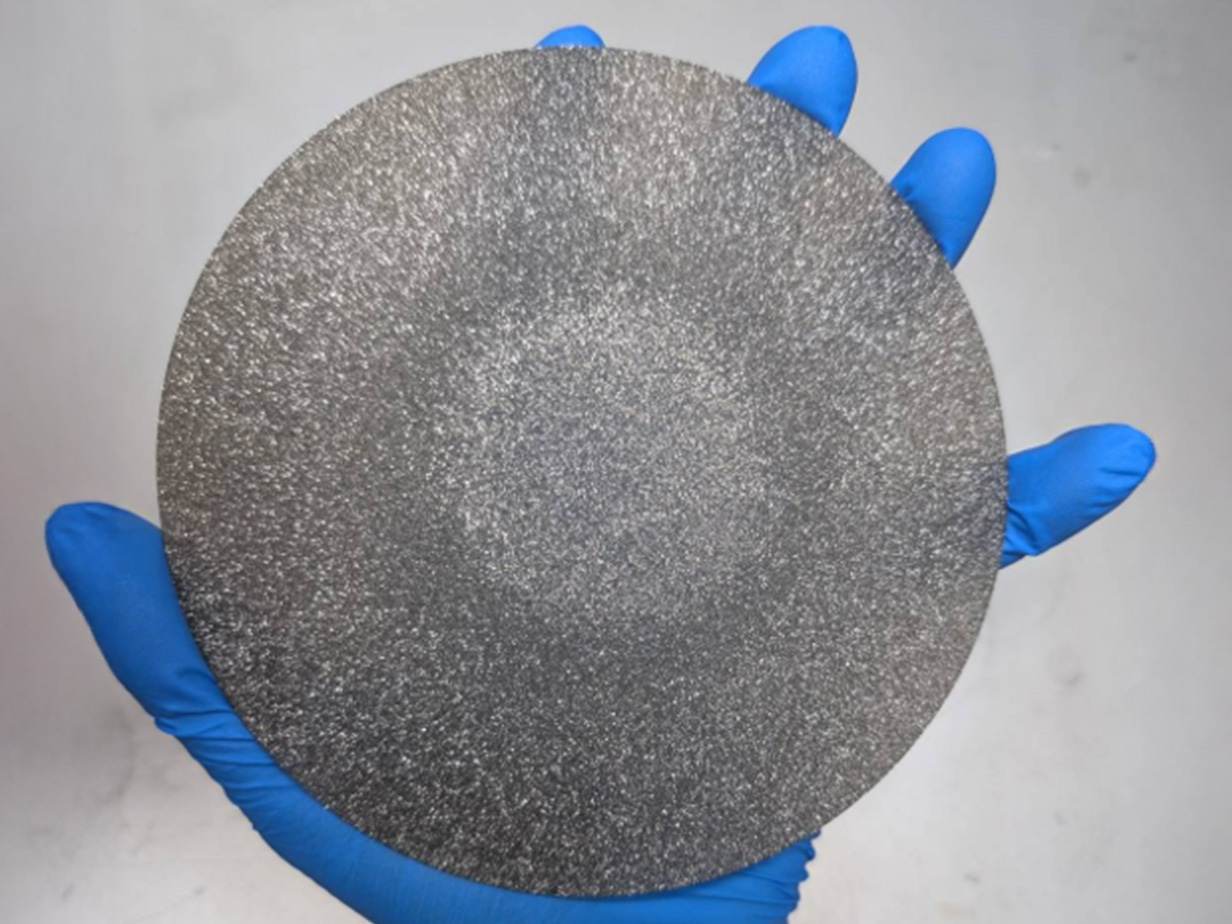
Mono Crystal Substrate
|
Type |
Product Model |
Thermal Conductivity* |
|
|
Mono-Crystalline |
CVD |
SDN0 |
2403 |
|
SDN0.25 |
2138 |
||
|
SDN0.5 |
1865 |
||
|
SDN2 |
1730 |
||
|
SDN4 |
1528 |
||
|
SDN8 |
1450 |
||
|
Poly-Crystalline |
CVD |
PDC1500 |
1530 |
|
PDC1200 |
1255 |
||
|
PDC1000 |
1051 |
||
|
PDD1000 |
1090 |
||
|
PDD800 |
825 |
||
|
HPHT |
PDH700 |
684 |
|
|
PDH600 |
494 |
||
|
複合材 |
壓鑄 |
CuD600 |
610 |
|
Metal |
- |
Cu |
400 |